The Future of Digital Technologies in Africa
What are digital technologies
Digital technologies are digital tools, systems, and processes such as hardware, software, and internet technology used for creating, storing, processing, and communicating information. These technologies directly influence data, work culture, skills, operations & processes, and many other aspects of organizations, brands, and businesses. The huge shift in digital innovations has led to increased internet penetration in Africa over the past years, resulting in better communication, creativity, and innovativeness. It has given a voice to a lot of voiceless people in Africa, most especially startups, who have leveraged the cloud in very effective and beneficial ways in saving cost and being more flexible.
Types of Digital Technologies
There are over 30 types of digital technologies, but those driving digital transformation include cloud computing, artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, the Internet of Things (IoT), blockchain, and big data analytics. These technologies span through manufacturing, communication, and business industries and greatly influence their processes, transactions, and outcomes.
Evolution of Digital Technologies
Cloud Computing
What is cloud computing? In simple terms, it is a user getting access to computer resources when they are in need. Computer resources include physical or virtual servers, data storage, networking capabilities, application development tools, software, AI-powered analytic tools, the internet, and more. These tools can be free or paid. Digital technologies use cloud computing to accomplish tasks like file storage, big data analytics, data backups and archiving, disaster recovery, software testing and development, infrastructure as a service (IaaS) and platform as a service (PaaS), communication, and social networking.
Evolution of cloud computing in this digital age: Cloud computing is counted as one of the prominent digital drivers, as it has greatly influenced data transformation. It has helped companies evolve in the way they create, analyze, store, and share information. Cloud computing solved the ancient problem of scalability, cost, and flexibility for businesses, brands, and individuals. Scalability in the sense that they can now create, analyze, and store more data due to more space to accommodate and analyze data; flexibility in that they could have 24/7 on-demand access to these resources; and cost-effectiveness in that they could now pay only for what they need. This greatly helped most especially SMEs in their information management. This can be further confirmed by the Flexera 2024 State of the Cloud report, which states that nearly half of all workloads and data are in the public cloud, and organizations’ usage of multi-cloud has gone up to 89% this year from 87% last year.”
Challenges to cloud computing
Cloud computing with all its solutions faces a consistent challenge
of information security where servers and sites are being attacked, also known as cyber security. Major causes of these attacks include but are not limited to weak and stolen credentials, backdoor and application vulnerabilities, malware, social engineering, too many permissions, ransomware, improper configuration and exposure via APIs, DNS attacks, and frequent changes in cloud offerings. Palo Alto Networks’ reports that four out of five security vulnerabilities observed in organizations across all sectors come from cloud environments. This report outlined the most common security flaws, of which 60% come from web framework takeover (22.8%), remote access services (20.8%), and IT security and networking infrastructure (17.1%). The report also highlights remedies to combat or control these attacks.
Future of cloud computing
Meanwhile, according to the Google Cloud Cyber Security Forecast 2024 report, the year 2024 will witness generative artificial intelligence and large language models (LLMs) being used in phishing and SMS and social engineering operations by attackers to spread fake news. In the insight report on the Global Cybersecurity Outlook 2024 published by the World Economic Forum in January 2024, the majority believe that “In the next two years, generative AI will provide cyber advantage to attackers (55.9%).
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
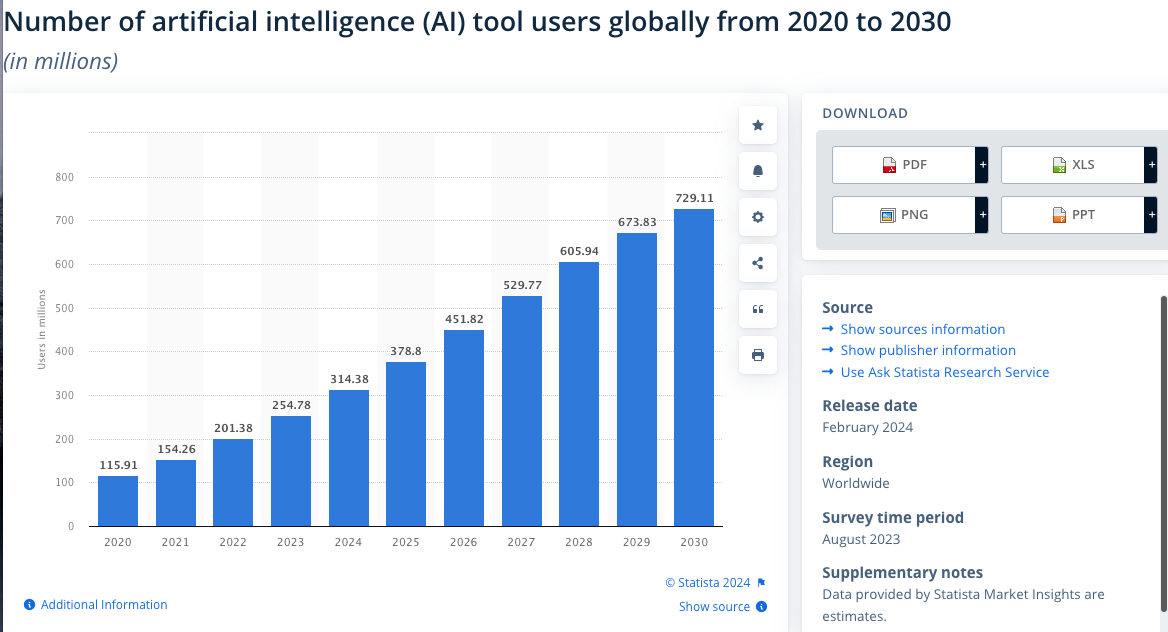
Reading through several definitions of AI online, I could come up with a summary definition of it being the ability of machines to think, act, and analyze written and verbal information like humans and work in an automated manner. AI stands in the center of digital technologies as it cuts through all industries. Digital technology in recent years has driven AI algorithms, though the future of AI is still ascertained. Companies are looking to automate their processes to be more efficient and cost-effective. Statista reports a 63% increase i
n the use of AI in the world from 2020 to 2024.
Rackspace technology also reports a global increase in usage and gains in AI from 2023 to 2024. Search logistics in a report on the status of AI in 2024 says AI makes jobs more efficient, with 79% of company executives saying AI is likely to simplify jobs and increase work efficiency. Among all these benefits, AI has some that are prone to challenges like increased regulation, data privacy concerns, and worries over job losses. Forbes predicts that AI will be unfathomably more powerful than humans in ways that will transform our world by 2030.
Internet of Things (IoT)
It refers to the collective network of connected devices and the technology that facilitates communication between devices and the cloud, as well as between the devices themselves. Consumer IoT eases daily life by connecting various devices to the internet, making them smarter and more responsive. Indmall highlights and details the 4 types of loT, which include consumer, commercial, industrial, and infrastructure loTs. The Internet of Things is useful for supply chain management, including inventory management, vendor relationships, fleet management, and scheduled maintenance. IoT is still needed in today’s digital edge and will be needed in the future.
Blockchain
Simplilearn describes blockchain technology as a structure that stores transactional records, also known as the block, of the public in several databases, known as the “chain,” in a network connected through peer-to-peer nodes. This technology was created for crypto currency data transmission and verification, but it has today been embarrassed by governments and big companies. Shiksha describes the evolution of blockchain from 1991 to 2024 and says it is gaining global recognition among millions of traders and researchers. Moreover, the technology is not limited to crypto finances anymore. It’s been spreading its roots in several other domains as well. According to reports by Statista, worldwide expenditure on blockchain solutions will increase from $4.5B in 2020 to $19B in 2024.
Big data analytics
Big data is the methods, tools, and applications used to collect, process, and derive insights from varied, high-volume, high-velocity data sets, coming from sources like the web, mobile, email, social media, and networked smart devices. The analysis from big data helps to uncover trends, patterns, and relationships in large amounts of raw data to help make data-informed decisions. Big data has changed the narrative of storing and analyzing information in caves, archives, and walls in the 90’s to today’s more fiscible and accommodating systems. Big data keeps evolving as trends in data and information change.
Conclusion
Digital technology indeed has its place in today’s and tomorrow’s society, and there is no doubt it will continuously help companies in Africa and the world to drive operational efficiency, improve customer experiences, foster innovation, and unlock new growth opportunities. The future of digital technology is envisioned to create new job and skill sets, especially in the fields of AI. Nevertheless, humanity has to be placed above machines and technology. No technology will surpass the importance of humans, as it was created by humans themselves. Thus, evolution in digital technology will have an even brighter future and effect, with a greater percentage of it being beneficial to the lay humans. In all the digital technologies making waves, we see that they aim to solve the problems of cost, feasibility, and security for companies and governments. From the look of things today, digital technologies are geared towards solving problems for companies and governments more than the layman on the street. It will be good if, in the future, there is a balance of technological solutions between companies, governments, and individuals.
Streamlining to Africa, digital technology has contributed to modernisation, innovation and has created room for collaboration. Africa should not lose guard on embrassing the upcoming opportunities in digital technologies. Africa should look at the financial benefits of these digital technologies and consider production more.
You can share your opinion in the comment section and read more interesting and trendy topics related to digitalisation here!